本教程可通过 Google Colab 交互运行!也可点击此处在本地运行 Jupyter Notebook。
快速入门
本教程面向刚接触 Apache TVM 的人群。采用简单的例子展示如何使用 Apache TVM 编译简单的神经网络。
目录
概述
Apache TVM 是一个机器学习编译框架,遵循Python 优先开发和通用部署的原则。 它接受经过预训练的机器学习模型,编译并生成可部署的模块,这些模块可以嵌入到任何地方运行。Apache TVM 还支持自定义优化过程,以引入新的优化方法、库、代码生成等。
Apache TVM 能够帮助您:
- 优化机器学习任务的性能,组合库与代码生成器。
- 部署机器学习任务至多种全新环境,包括新运行时和新硬件。
- 持续改进与定制 Python 中的机器学习部署流程,通过快速定制库调度、引入定制算子与代码生成方式。
完整流程
我们将展示使用 Apache TVM 编译神经网络模型的完整流程,包括如何优化、部署和运行模型。整体流程如下图所示:
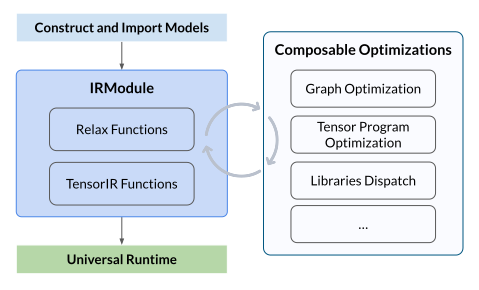
整体流程包括以下几个步骤:
- 构建或导入模型:可以手动构建一个神经网络模型,或从其他框架(如 PyTorch、ONNX)中导入一个预训练模型,并生成 TVM 的 IRModule。该模块包含编译所需的所有信息,包括用于表示计算图的高层 Relax 函数,以及用于描述张量程序的低层 TensorIR 函数
- 执行可组合优化:执行一系列优化转换,包括计算图优化、张量程序优化和算子调度/分发等
- 构建并进行通用部署:将优化后的模型构建为可部署模块,使用 TVM 通用运行时在不同设备上运行,例如 CPU、GPU 或其他加速器
构建或导入模型
在开始之前,让我们先构建一个神经网络模型。在本教程中,为了简化操作,我们将使用 TVM Relax 前端(这是一个类似 PyTorch 的 API )直接在脚本中定义一个两层的 MLP(多层感知器)网络。
import tvm
from tvm import relax
from tvm.relax.frontend import nn
class MLPModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(MLPModel, self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(784, 256)
self.relu1 = nn.ReLU()
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(256, 10)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.relu1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
return x
然后我们可以将模型导出为 TVM IRModule,这是 TVM 中的核心中间表示。
mod, param_spec = MLPModel().export_tvm(
spec={"forward": {"x": nn.spec.Tensor((1, 784), "float32")}}
)
mod.show()
输出:
# from tvm.script import ir as I
# from tvm.script import relax as R
@I.ir_module
class Module:
@R.function
def forward(x: R.Tensor((1, 784), dtype="float32"), fc1_weight: R.Tensor((256, 784), dtype="float32"), fc1_bias: R.Tensor((256,), dtype="float32"), fc2_weight: R.Tensor((10, 256), dtype="float32"), fc2_bias: R.Tensor((10,), dtype="float32")) -> R.Tensor((1, 10), dtype="float32"):
R.func_attr({"num_input": 1})
with R.dataflow():
permute_dims: R.Tensor((784, 256), dtype="float32") = R.permute_dims(fc1_weight, axes=None)
matmul: R.Tensor((1, 256), dtype="float32") = R.matmul(x, permute_dims, out_dtype="void")
add: R.Tensor((1, 256), dtype="float32") = R.add(matmul, fc1_bias)
relu: R.Tensor((1, 256), dtype="float32") = R.nn.relu(add)
permute_dims1: R.Tensor((256, 10), dtype="float32") = R.permute_dims(fc2_weight, axes=None)
matmul1: R.Tensor((1, 10), dtype="float32") = R.matmul(relu, permute_dims1, out_dtype="void")
add1: R.Tensor((1, 10), dtype="float32") = R.add(matmul1, fc2_bias)
gv: R.Tensor((1, 10), dtype="float32") = add1
R.output(gv)
return gv
执行优化转换
Apache TVM 利用 pipeline 来转换和优化程序。该 pipeline 封装了一系列转换,同时实现两个目标(在同一层级):
- 模型优化: 如算子融合、布局重写等
- 张量程序优化: 将算子映射到低层实现(包括库或代码生成)
这两个是目标而非 pipeline 的阶段。这两种优化是在同一层级进行的, 或者可以分两个阶段单独进行。
在本教程中,我们仅展示整体流程,使用 zero 优化 pipeline,而不针对任何特定目标进行优化。
mod = relax.get_pipeline("zero")(mod)
构建和通用部署
优化完成后,我们可以将模型构建为可部署模块,并在不同设备上运行。
import numpy as np
target = tvm.target.Target("llvm")
ex = tvm.compile(mod, target)
device = tvm.cpu()
vm = relax.VirtualMachine(ex, device)
data = np.random.rand(1, 784).astype("float32")
tvm_data = tvm.runtime.tensor(data, device=device)
params = [np.random.rand(*param.shape).astype("float32") for _, param in param_spec]
params = [tvm.runtime.tensor(param, device=device) for param in params]
print(vm["forward"](tvm_data, *params).numpy())
输出:
[[24622.611 24500.982 24233.826 24980.064 26626.14 24752.494 25216.44
25364.43 24566.611 25446.244]]
我们的目标是以最小的运行时支持,将机器学习引入到任何感兴趣的语言的应用程序中。
- IRModule 中的每个函数在运行时都成为可执行函数。例如在 LLM 场景中,我们可以直接调用
prefill和decode函数。
prefill_logits = vm["prefill"](inputs, weight, kv_cache)
decoded_logits = vm["decode"](inputs, weight, kv_cache)
- TVM 运行时自带原生数据结构,如 NDArray,也可以与现有生态系统进行零拷贝交换(通过 DLPack 与 PyTorch 交换)。
# 将 PyTorch 张量转换为 TVM NDArray
x_tvm = tvm.runtime.from_dlpack(x_torch)
# 将 TVM NDArray 转换为 PyTorch 张量
x_torch = torch.from_dlpack(x_tvm)
- TVM 运行时可在非 Python 环境中工作,因此也适用于移动设备等场景。
// C++ 代码片段
runtime::Module vm = ex.GetFunction("load_executable")();
vm.GetFunction("init")(...);
Tensor out = vm.GetFunction("prefill")(data, weight, kv_cache);
// Java 代码片段
Module vm = ex.getFunction("load_executable").invoke();
vm.getFunction("init").pushArg(...).invoke;
Tensor out = vm.getFunction("prefill").pushArg(data).pushArg(weight).pushArg(kv_cache).invoke();
后续阅读
本教程演示了使用 Apache TVM 编译神经网络模型的整体流程。如需了解更高级或具体的主题,请参考以下教程(可右键另存为下载):